
Name the clement which does not contain any neutrons in its nucleus.Įlement is Hydrogen. In the different orbits or shells in one atom of aluminium. The atom of aluminium is represented by 27Al 13. Calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine. Ordinary chlorine gas has two isotopes : 35 17Cl and 37 17Cl in the ratio of 3 : 1. has 4 electrons in the outermost orbit.W – atomic number = of electrons = 9 (2, 7)Įlements X, Y, Z have atomic numbers 6, 9 and 12 respectively. Write down the formula of the compound formed by atoms X and Y.Which one of these atoms (1) contains 7 protons (2) has an electronic configuration 2, 7 ?.When molten magnesium chloride is electrolysed suitable anode used is carbon.Two isotopes of chlorine have same chemical reactions as their atomic number i.Number electrons in chlorine atom is 17 and their distribution in various shells in K = 2, L = 8, M = 7.ģ5 17Cl number of protons = 17 and number neutrons = 35 – 17 = 18.Atomic number is the number of protons in an atom.Ītom : The basic unit of matter is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction.If molten magnesium chloride is electrolysed suggest a suitable electrode.Explain why the two atoms in (iii) above have the same chemical reactions.State the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in the following isotopes: 35Cl 17, 37Cl 17.Write down the electronic configuration of the chlorine atom.What is meant by “atomic number of an element” ? What do you understand by an ‘atom’.It is a mixture of two isotopes having mass number of 35 and 37. give the reason why the two isotopes of magnesium have different mass numbers.Ĭhlorine is an element of atomic number 17.Compare the ‘ atoms of these isotopes with respect to : Number of electrons = P = e = 16 Question 1.(1987)Ģ4 12Mg and 26 12Mg are symbols of two isotopes of magnesium.

Give a simple diagram to show the arrangement of the electrons in an atom of sulphur. State the number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of sulphur.
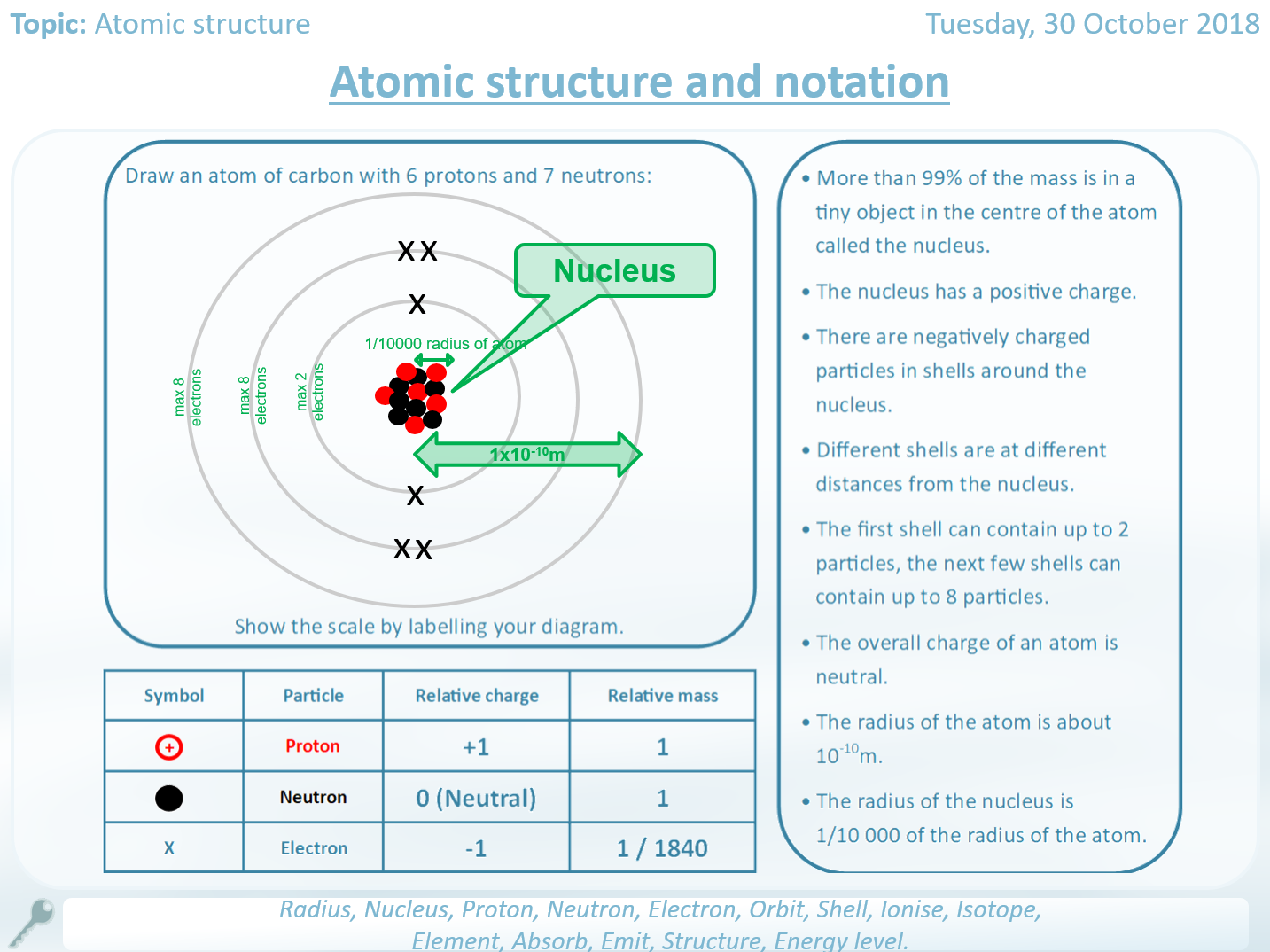
Sulphur has an atomic number of 16 and a mass number of 32. Mass number : “Is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom of an element.”Įlectron : “A sub-atomic particle having a unit negative charge and mass equal to 1/1837 of that of hydrogen atom, revolve round the nucleus.” įrom the symbol 4/2 He for the element helium, write down the mass number and the atomic number of the element. OR “Is the number of electrons in the complete atom.” OR “Is the number of positive charges in the nucleus of its atom.” Thus there are two atoms attached to each fcc lattice point: One located just at the position of the lattice point and one being shifted by the vector $$.Define the terms : atomic number, mass number and electron.Ītomic number : “Is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.” But when we choose a proper perspective, we can see that the underlying structure is actually a fcc structure with a two-atomic basis. The structure is not a Bravais lattice by itself because there are two types of lattice points with different environments. How can this structure be classified in our previous classification (14 Bravais lattices)? Tetrahedrical structure of diamond: Each atom forms bonds with four nearest neighbours (enclosed angles are 109.47°). Therefore it is evident that such atoms try to form a three-dimensional structure in which every atom has four uniformly distributed nearest neighbours as binding partners. This rearrangement entails initially some energy expense but afterwards the atoms are able to form four very strong covalent bond which compensate this expense by far. However, it is possible that these orbitals merge and form four new equivalent so-called sp3 hybrid orbitals all being only half-filled. One could in principle expect that these atoms have a filled s orbital and two half-filled p orbitals. Remember that the common feature of these elements is the electron configuration of the outer shell: Besides carbon these are germanium and silicon which are both very important for semiconductor physics. In this article we will have a look at the crystal structure which is formed by many elements of the 4th main group of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
